Understanding Inflammation and Its Effects on the Body
Inflammation is a natural process that occurs in our bodies as a response to harmful stimuli, such as injury, infection, or irritants. It is an essential part of our immune system's defense mechanism, helping to protect us from further damage and facilitate healing. However, when inflammation persists and becomes chronic, it can have detrimental effects on our overall health, including an increased risk of developing cancer. In this article, we will explore the connection between cancer and chronic inflammation, as well as discuss ways to reduce inflammation and lower your risk of cancer.
The Role of Inflammation in Cancer Development
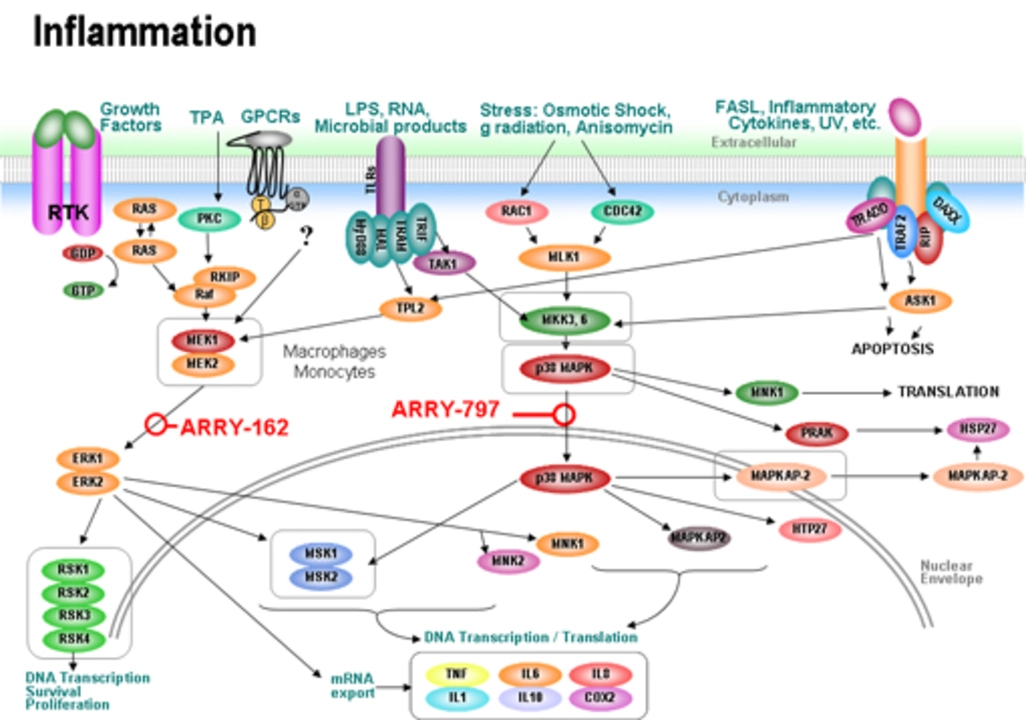
Chronic inflammation has been linked to the development of various types of cancer, including those of the colon, lung, breast, and liver. This is because prolonged inflammation can lead to DNA damage in cells, which in turn can cause mutations that result in the formation of tumors. Additionally, the presence of chronic inflammation can create an environment that promotes tumor growth and survival. For example, inflammatory cells can release signaling molecules called cytokines that can stimulate the growth of blood vessels, providing tumors with the nutrients they need to grow and spread.
Factors That Contribute to Chronic Inflammation
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of chronic inflammation in the body. Some of these include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to an increased production of inflammatory cytokines, contributing to a chronic inflammatory state.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains numerous harmful chemicals that can cause inflammation in the lungs and other tissues.
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to inflammation in the liver and other organs.
- Poor diet: Diets high in processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars can contribute to inflammation in the body.
- Chronic infections: Long-term infections, such as hepatitis B and C, can cause chronic inflammation and increase the risk of cancer.
Preventing Chronic Inflammation and Reducing Cancer Risk
Since chronic inflammation is closely linked to an increased risk of cancer, it is important to take steps to reduce inflammation in the body. Here are some lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent chronic inflammation and lower your risk of developing cancer:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing excess weight and maintaining a healthy body weight can help to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Quit smoking: Giving up tobacco can significantly lower your risk of developing chronic inflammation and cancer.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol in moderation or not at all can help to reduce inflammation and cancer risk.
- Eat a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help to reduce inflammation and lower your risk of cancer.
- Get regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Incorporate into Your Diet
There are certain foods that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, meaning they can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Some of these include:
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and other fatty fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation.
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are high in antioxidants and other nutrients that can help to reduce inflammation.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and other berries are packed with antioxidants that can help to combat inflammation.
- Nuts and seeds: Walnuts, almonds, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are rich in healthy fats and other nutrients that can help to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Spices and herbs: Turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon are just a few examples of spices and herbs that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties.
Monitoring Inflammatory Markers in the Body
There are some blood tests that can be performed to measure the level of inflammation in your body. One of these tests is called the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, which measures the amount of CRP in your blood. High levels of CRP can indicate the presence of inflammation in the body. Another test is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, which measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube. A faster settling rate can indicate inflammation. Regularly monitoring these markers can help you and your healthcare provider assess your risk of developing chronic inflammation and cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there is a strong connection between cancer and chronic inflammation. By understanding the factors that contribute to chronic inflammation and taking steps to reduce inflammation in the body, you can lower your risk of developing cancer. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, eating a balanced diet, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your meals. Regularly monitoring inflammatory markers can also help you and your healthcare provider track your progress in reducing inflammation and lowering your cancer risk.



Tara Newen
13 May 2023 - 17:55 PM
Look, the link between chronic inflammation and cancer isn’t some new fad-it's been backed by decades of epidemiological data. Excess adipose tissue releases pro‑inflammatory cytokines like IL‑6 and TNF‑α, which can punch holes in DNA and set the stage for oncogenesis. Smoking introduces a cocktail of oxidants that keep the immune system in a constant state of alarm, and that alarm is precisely what fuels tumor microenvironments. If you keep popping pills instead of addressing the root causes, you’re just postponing the inevitable. So, before you start preaching about “miracle diets,” recognize that lifestyle overhaul trumps any supplement you can find on the internet.
Amanda Devik
13 May 2023 - 19:02 PM
Hey fam, this article really hits the sweet spot where science meets everyday action. The cascade of cytokines we talk about isn’t just lab jargon; it’s the body’s alarm system that can be dialed down with proper nutrition and movement. Think of omega‑3s as the peacekeepers that calm the storm, while processed sugars act like provocateurs stirring the fire. When you swap a soda for a berry‑rich smoothie, you’re literally turning down the volume on a tumor‑friendly soundtrack. Keep the momentum rolling, stay curious, and let those anti‑inflammatory foods do the heavy lifting.
Mr. Zadé Moore
13 May 2023 - 20:00 PM
Chronic inflammation creates a pro‑tumorigenic microenvironment. Persistent cytokine release sustains NF‑κB activation. NF‑κB drives transcription of survival genes. DNA repair mechanisms become overwhelmed by oxidative stress. Reactive oxygen species induce point mutations. Angiogenic factors like VEGF are upregulated. New vasculature delivers nutrients to nascent tumors. Immune surveillance is compromised by regulatory T cells. Myeloid‑derived suppressor cells inhibit cytotoxic activity. Epigenetic modifications silence tumor suppressor loci. Chronic exposure to carcinogens amplifies mutational load. Obesity‑derived leptin reinforces inflammatory loops. Smoking introduces polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons that act as mutagens. Alcohol metabolism generates acetaldehyde, a DNA‑adduct former. Lifestyle interventions can attenuate these pathways if consistently applied.
Brooke Bevins
13 May 2023 - 20:50 PM
Totally agree – inflammation is no joke! 😊
Vandita Shukla
13 May 2023 - 21:32 PM
Honestly, the “miracle” claim is overblown. The real issue is that most people underestimate how processed carbs spike insulin, which then fuels inflammatory pathways via mTOR. If you’re not counting hidden sugars in sauces and breads, you’re basically feeding the fire. The literature shows a clear dose‑response between refined carbohydrate intake and CRP levels. So stop treating diet advice as optional; it’s a non‑negotiable part of cancer prevention.
Tom Saa
13 May 2023 - 22:13 PM
One could argue that inflammation is the body’s existential protest against entropy, a silent scream that, when chronic, morphs into a catalyst for malignancy. The relentless NF‑κB signaling mirrors our own relentless pursuit of meaning, yet without balance it spirals into chaos. It’s poetic, in a grim way, that the same pathways meant to heal become the architects of decay. Perhaps the lesson lies in recognizing the duality of our internal fire and learning to temper it with mindful restraint.
Andrea Mathias
13 May 2023 - 22:55 PM
Look, we don’t need some foreign “miracle diet” hype to tell us that obesity is a ticking time bomb. The American way of life-fast food, big portions, and zero accountability-creates the perfect breeding ground for chronic inflammation. If you’re still buying into the hype that a single supplement will fix it, you’re just feeding the propaganda machine. Get real, cut the junk, and stop blaming the system for what you’re choosing to ignore.
TRICIA TUCKER
13 May 2023 - 23:37 PM
Hey everyone, just wanted to add a quick note on the importance of clear communication when discussing health topics. Using proper punctuation and grammar helps ensure that the science isn’t lost in the noise. It’s also a great way to make the information more accessible to folks who might be new to the subject. Let’s keep our comments friendly and easy to read for the whole community.
Dave Tu
14 May 2023 - 00:18 AM
While I appreciate the emphasis on linguistic precision, it is essential to acknowledge that formal diction does not inherently guarantee scientific accuracy. The risk lies in allowing style to eclipse substance, especially when complex mechanisms such as cytokine cascades are at stake. Therefore, a balance must be struck between eloquence and rigorous fact‑checking.
Johnna Sutton
14 May 2023 - 01:00 AM
Indeed, the pursuit of eloquence should never supplant the veracity of data, yet one must also recognize that the prevailing narrative is often manipulated by hidden agencys seeking profit. By ignoring the subtle cues embedded within the literature, we risk becoming pawns in a larger agenda. It’s imperative we maintain vigilance, even when the language appears polished.
Sam Rail
14 May 2023 - 01:42 AM
Nice rundown, I’ve been trying to cut back on soda and feel a bit more energetic.
Christine Watson
14 May 2023 - 02:23 AM
That’s awesome! Small changes like swapping sugary drinks for water can swing your CRP levels down and boost overall vitality. Keep at it, and you’ll likely notice even more benefits as your body adjusts.
Macy Weaver
14 May 2023 - 03:05 AM
It’s fascinating how a simple habit shift can cascade into systemic improvements, especially when the immune system regains its equilibrium. Maintaining that momentum by pairing hydration with regular movement will further reinforce the anti‑inflammatory response.
Blake Marshall
14 May 2023 - 03:47 AM
People keep forgetting that the biggest driver of chronic inflammation is actually the gut microbiome, not just the obvious stuff like smoking or weight. If you screw up your gut flora with antibiotics or bad diet, you’re basically inviting systemic inflammation to set up shop.
Shana Shapiro '19
14 May 2023 - 04:28 AM
I understand how overwhelming it can feel to manage gut health alongside other lifestyle changes. A gentle approach, such as incorporating probiotic foods and fiber, can gradually restore balance without adding stress.
Jillian Bell
14 May 2023 - 05:10 AM
Don’t be fooled by the mainstream narrative that praises probiotics as a simple fix; it’s a distraction crafted by big pharma to keep us buying cheap supplements while the real manipulations continue behind the scenes. The truth about gut health is buried under layers of controlled research, and only those who look beyond the official storyline can see the hidden agenda.