Introduction to Heparin Sodium and Liver Disease
As someone living with liver disease, it's important to understand how different medications may affect your condition. One such medication is heparin sodium, a widely used anticoagulant that can help prevent blood clots. In this article, we will explore the relationship between heparin sodium and liver disease, discussing what patients need to know to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Understanding Heparin Sodium
Heparin sodium is a type of anticoagulant medication, which means it helps to prevent blood clots from forming. It's commonly prescribed for patients who are at risk of developing blood clots due to medical conditions or surgical procedures. Heparin sodium works by inhibiting certain proteins in the blood that are responsible for clotting, thereby reducing the risk of clot formation.
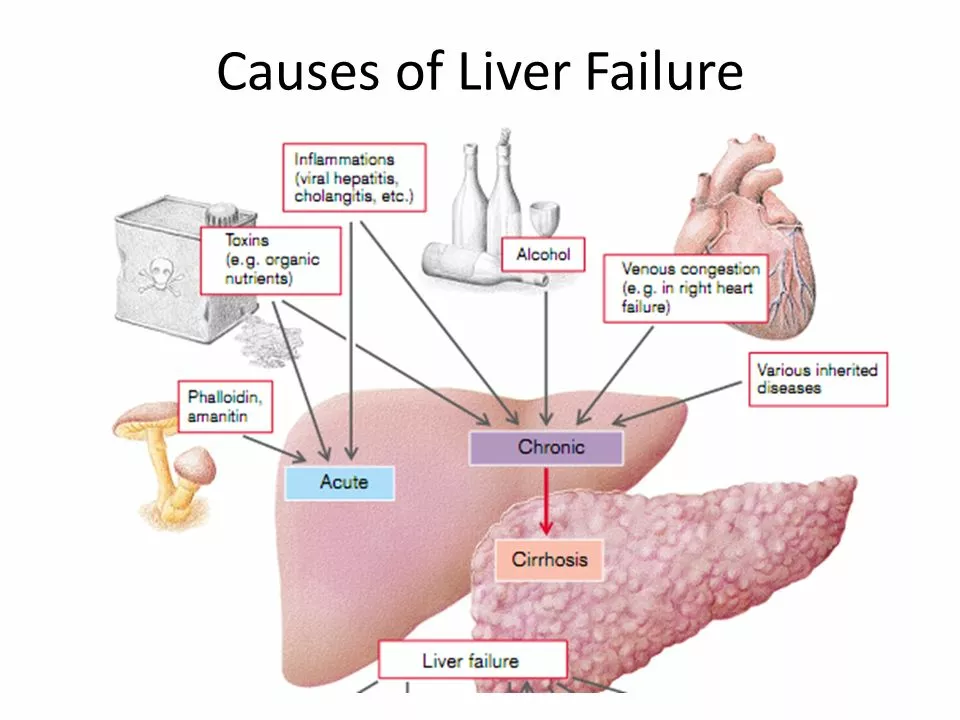
How Liver Disease Affects Blood Clotting
Liver disease can have a significant impact on your body's ability to form blood clots. The liver is responsible for producing many of the proteins involved in the clotting process, so when it's not functioning properly, this can lead to an increased risk of bleeding and clotting issues. This is one reason why it's important for patients with liver disease to be aware of their treatment options when it comes to anticoagulant medications like heparin sodium.
Benefits of Heparin Sodium for Liver Disease Patients
For some patients with liver disease, heparin sodium may offer important benefits. Because liver disease can impair the body's natural ability to form blood clots, using an anticoagulant medication like heparin sodium can help to reduce the risk of dangerous clotting events. This can be particularly important for patients who are undergoing surgical procedures, as the risk of blood clots can be higher in these situations.
Considerations When Using Heparin Sodium
While heparin sodium can offer benefits for some liver disease patients, it's important to consider the potential risks as well. For example, because heparin sodium is an anticoagulant, it can increase the risk of bleeding, which may be a concern for patients with liver disease who already have an impaired clotting ability. Additionally, heparin sodium can sometimes cause a decrease in platelet count, which can further increase the risk of bleeding.
Monitoring Heparin Sodium Therapy in Liver Disease Patients
For patients with liver disease who are prescribed heparin sodium, close monitoring is essential to ensure the medication is both safe and effective. This may include regular blood tests to check for any changes in clotting factors or platelet count, as well as monitoring for any signs of bleeding or clotting complications. It's important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to ensure they're receiving the appropriate dose of heparin sodium and that their condition is being closely monitored.
Alternatives to Heparin Sodium for Liver Disease Patients
In some cases, an alternative to heparin sodium may be recommended for patients with liver disease. This could include other anticoagulant medications, such as low molecular weight heparins or direct oral anticoagulants. The choice of medication will depend on a variety of factors, including the patient's specific medical condition and the potential risks and benefits of each option. It's important for patients to discuss their treatment options with their healthcare team to determine the best course of action for their individual needs.
Managing Bleeding Risks with Heparin Sodium and Liver Disease
For patients with liver disease who are taking heparin sodium, managing the risk of bleeding is a crucial aspect of their care. This may involve regular blood tests to monitor clotting factors, as well as taking steps to minimize the risk of injury or bleeding. Patients should be sure to follow their healthcare provider's recommendations regarding any precautions they should take to reduce their risk of bleeding complications.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Team
As a patient with liver disease, it's important to maintain open communication with your healthcare team about your treatment options, including the use of heparin sodium. Be sure to discuss any concerns you may have about the medication and its potential risks and benefits, and ask any questions you may have about your condition and treatment plan. Working closely with your healthcare team can help ensure you receive the best possible care and optimize your chances of successfully managing your liver disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between heparin sodium and liver disease is essential for patients who may be prescribed this medication. By being aware of the potential benefits, risks, and considerations when using heparin sodium, patients with liver disease can make informed decisions about their treatment options and work closely with their healthcare team to ensure their condition is effectively managed. Remember, open communication with your healthcare team is key to receiving the best possible care for your liver disease.





Nicole Koshen
6 May 2023 - 20:35 PM
Understanding how heparin interacts with liver disease is crucial. Regular blood work helps spot any shifts in clotting factors early.
Patients should keep a log of any bruising or unusual bleeding and share it with their doctor.
Open communication with the healthcare team ensures dose adjustments are made promptly.
It's also wise to discuss alternative anticoagulants if bleeding risks become a concern.
Staying informed empowers patients to manage their condition effectively.
Ed Norton
7 May 2023 - 17:09 PM
Heparin can be tricky for liver patients.
Karen Misakyan
8 May 2023 - 13:42 PM
The interplay between anticoagulation therapy and hepatic insufficiency warrants rigorous scrutiny.
The hepatic synthesis of clotting factors is diminished, rendering the hemostatic balance precarious.
Consequently, heparin administration must be calibrated with heightened vigilance.
Pharmacokinetic alterations in cirrhotic patients may prolong the half‑life of unfractionated heparin.
Such prolongation potentiates the risk of iatrogenic hemorrhage.
Monitoring activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) remains the cornerstone of dosage adjustment.
Nonetheless, aPTT values may be confounded by reduced antithrombin III levels inherent to liver disease.
Therefore, anti‑Xa assays provide a more reliable metric in this cohort.
Dose reduction is advisable when platelet counts descend below the conventional threshold.
Moreover, clinicians should remain alert to heparin‑induced thrombocytopenia, which can masquerade as liver‑related cytopenia.
The decision to employ low molecular weight heparin versus unfractionated heparin should consider renal clearance as well.
In patients with concomitant renal impairment, unfractionated heparin offers a reversible option.
Patient education regarding signs of bleeding, such as ecchymoses or melena, is indispensable.
Interdisciplinary coordination among hepatologists, hematologists, and pharmacists optimizes therapeutic outcomes.
Ultimately, individualized risk‑benefit analysis underpins the safe use of heparin in hepatic pathology.
Amy Robbins
9 May 2023 - 10:15 AM
Oh great, another "miracle drug" that supposedly works for everyone except the folks whose liver is already a mess.
Sure, let’s throw heparin in the mix and hope the bleeding doesn’t turn into a full‑blown disaster.
If you think a simple blood test can catch all the nuances, you’re living in a fantasy world.
Probably best to keep the meds to yourself until the next headline screams "new side effect".
Michelle Zhao
10 May 2023 - 06:49 AM
While many herald heparin as a panacea for clot prevention, one must ponder the paradox it presents to those with compromised hepatic function.
Is it not a theatrical irony that a drug designed to halt clot formation may simultaneously amplify hemorrhagic tendencies in a liver already on the brink?
One could argue that the drama lies not in the medication itself but in the overconfidence of prescribers who neglect the fragile balance within these patients.
Nevertheless, the decision remains a delicate choreography between risk and reward.
Eric Parsons
11 May 2023 - 03:22 AM
For patients with liver disease, it’s essential to individualize heparin dosing based on serial aPTT or anti‑Xa levels.
Regular monitoring can catch early signs of over‑anticoagulation, which is especially important given the reduced synthesis of clotting factors.
Consulting a hepatology‑trained pharmacist can also help navigate drug‑drug interactions and adjust dosing accordingly.
Overall, a collaborative approach reduces the chance of bleeding complications.
Mary Magdalen
11 May 2023 - 23:55 PM
Let’s cut through the jargon: heparin can be a double‑edged sword for liver patients, slicing clot risk while slashing platelet reserves.
If you’re not vigilant, you’ll end up with a cascade of bruises that could have been avoided with smarter dosing.
Colorful language aside, the bottom line is that vigilant labs and a keen eye on bleeding are non‑negotiable.
Dhakad rahul
12 May 2023 - 20:29 PM
Heparin drama? Absolutely! 🎭
Picture this: a liver‑stricken patient sitting on the edge of a cliff, and heparin is the rope that might snap at any moment.
Yet some clinicians act like it’s a safety net that never fails.
🥀 Let’s not forget the emotional toll when the rope frays and bleeding ensues!
William Dizon
13 May 2023 - 17:02 PM
It's great to see the emphasis on monitoring; keeping patients informed about signs of bleeding really makes a difference.
Encouraging open dialogue with doctors ensures any dosage tweaks happen swiftly.
Having a clear plan for lab work can reduce anxiety for those navigating both liver disease and anticoagulation.
Jenae Bauer
14 May 2023 - 13:35 PM
Some might say the whole heparin regimen is a tale spun by pharmaceutical giants to keep profits flowing.
What if the “monitoring” labs are just a smokescreen, diverting attention from hidden side‑effects?
Consider the possibility that the data we rely on are selectively published to mask a larger safety issue.
Stay vigilant, question the narrative, and demand full transparency.
vijay sainath
15 May 2023 - 10:09 AM
Dude, the whole thing is basic – you get heparin, you get bloodwork, you avoid bleeding. No need for a lecture.
Just tell them to get the tests done and stop overcomplicating it.
Daisy canales
16 May 2023 - 06:42 AM
Sure, keep an eye on the labs, but don’t panic if you see a tiny dip.
keyul prajapati
17 May 2023 - 03:15 AM
The management of anticoagulation in the setting of hepatic insufficiency is a nuanced endeavor that benefits from a systematic, evidence‑based approach.
First, it is imperative to establish baseline coagulation parameters, including prothrombin time, INR, and platelet count, prior to initiating therapy.
Subsequent monitoring should be individualized, with a preference for anti‑Xa levels in patients where antithrombin deficiency may render aPTT less reliable.
In cases of significant thrombocytopenia, dose reduction or transition to an alternative anticoagulant may be warranted.
Renal function must also be assessed, as it influences the pharmacokinetics of low molecular weight heparin.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration among hepatology, hematology, and pharmacy services enhances safety and efficacy.
Patient education remains a cornerstone, emphasizing the importance of reporting any signs of bleeding promptly.
Ultimately, diligent monitoring, dose titration, and clear communication form the pillars of optimal care for these complex patients.
Alice L
17 May 2023 - 23:49 PM
From a cultural standpoint, it is essential to recognize that patients from diverse backgrounds may have varying levels of health literacy regarding anticoagulation therapy.
Providing information in a culturally sensitive manner can greatly enhance adherence and understanding.
Seth Angel Chi
18 May 2023 - 20:22 PM
While the article covers basics, it glosses over the importance of anti‑Xa monitoring in cirrhotic patients.
Neglecting this detail can lead to suboptimal dosing.
Kristen Ariies
19 May 2023 - 16:55 PM
Fantastic overview!,, however, remember,, regular lab checks,, vigilant monitoring,, and clear communication with your care team are absolutely vital,, especially when navigating the complexities of liver disease and anticoagulation!
Mary Latham
20 May 2023 - 13:29 PM
hey guys i think heparin is ok but make sure u get your bloodwork done regularly lol
Marie Green
21 May 2023 - 10:02 AM
Sounds like a careful plan is key, staying aware of any bruises or unusual bleeding can really help.
TOM PAUL
22 May 2023 - 06:35 AM
Curious about how different liver disease stages affect heparin metabolism – does anyone have insights on dosing adjustments for early versus advanced fibrosis?
Ash Charles
23 May 2023 - 03:09 AM
Listen up – don’t screw around with heparin doses unless you’ve got a solid lab backing. Aggressive monitoring isn’t optional.