Health consequences: how meds, supplements, and habits affect your body
Want straight talk about how medicines and everyday choices change your health? This page collects practical, no-nonsense advice. You’ll learn the common risks to watch for, simple ways to limit harm, and when to call a professional.
Common medication risks you should know
Every drug has intended effects and possible side effects. Some are mild—like nausea with certain antibiotics. Others are serious, such as low blood pressure or dangerous interactions between prescriptions. For example, mixing cephalexin with alcohol may not be dramatic, but other antibiotics and drugs can make you very sick. Birth control pills like desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol can change how your body absorbs vitamins, which can show up as low energy or mood changes if you don’t adjust your diet or supplements.
Some meds interact in surprising ways. Febuxostat used for gout can clash with other prescriptions. Clonidine can lower blood pressure and cause dizziness or sleepiness. Antidepressant strategies, like adding bupropion to an SSRI, can help but bring new side effects and require close monitoring. Always check for interactions before adding anything new—even over-the-counter drugs, herbal products, or vitamins.
Spot trouble early and act
How do you know something’s wrong? Watch for sudden changes: blood pressure swings, severe stomach pain, breathing trouble, allergic rashes, or new mental symptoms like extreme confusion. Keep a list of every drug and supplement you take. Share that list with any provider or pharmacist. If a new symptom starts soon after changing meds, consider it a red flag and contact your prescriber.
Practical checks you can do today: read the patient leaflet, use an interaction checker (many pharmacy apps do this), and ask your pharmacist about common combos to avoid. If cost pushes you to switch pharmacies or buy online, choose reputable sites and verify the medication’s name, dose, and origin. Cheap is not worth a dangerous mistake.
Some consequences take longer to appear. Long-term use of certain drugs can deplete nutrients or affect organs. Diuretics may change potassium levels; long-term antibiotics can affect gut flora. Ask for baseline tests when starting medicines that can impact liver, kidneys, or electrolytes. Small lab checks catch problems early.
Final quick tips: don’t mix alcohol with meds unless you’ve checked it’s safe, tell every provider about supplements, report new or worsening symptoms fast, and use secure apps or your pharmacist to check prices without risking unsafe sources. If you’re unsure, ask—your health depends on the small choices you make every day.
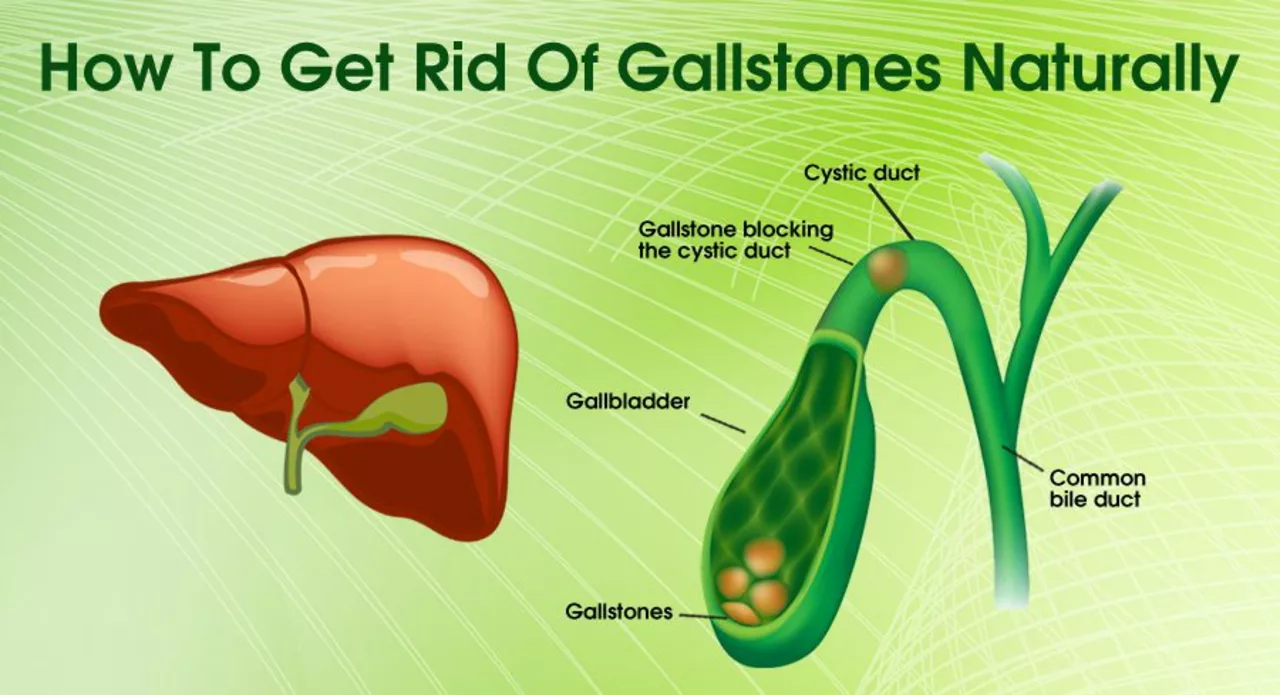
The Long-Term Effects of Living with Gallstones
Living with gallstones for an extended period can have significant long-term effects on one's overall health. Constant pain and discomfort become a daily struggle, affecting our ability to perform everyday tasks and enjoy life. Additionally, if left untreated, gallstones can lead to severe complications such as gallbladder inflammation, infection, and even pancreatitis. Moreover, the risk of gallbladder cancer increases with the presence of gallstones. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss treatment options and prevent these long-term consequences.
Read More